SEO and SERP explained, plus SEO tips for your website
Your favourite search engines like Google, Yahoo! and Bing use complex algorithms to show you the best answers to your question or search phrase. In fact, they maintain extreme secrecy about their algorithm and they never share the exact ranking factors.
Luckily, web users and SEO experts have worked out most of the details, so we can tell you how search engines work, and how to make your website rank better in search.
The basics of how search engines work
Each time you type a search, thousands of results come up in a matter of seconds, maybe even fractions of a second. This is because the search engines have already crawled millions of pages and ranked them for different phrases.
Search engines rank websites in order of how well they match the search keywords or phrases, with the top result being the most relevant to your search query.
Here is the process in a nutshell:
- Search engine bots (or spiders) crawl all the pages on the internet and look at content
- Crawlers add pages to their index and catalogue them, noting the topics and keywords for each page
- When people conduct a search, the search engine shows them the best results based on their search phrase
Now let’s look in a bit more detail.
Crawling and Indexing
The search engine’s bot (or spider) visits and crawls web pages and looks at the content. The bot considers:
- Words and phrases used in the headings, text and image descriptions of the page
- Links to and from the page, and the words in the text of those links
- The website’s sitemap, which shows the structure and hierarchy of all the pages in a website, and how they link to each other
- The website’s robots.txt file, which tells the bot which pages it’s allowed to see, and which pages it’s not meant to visit or inspect (such as 404 error pages, password protected pages and non-index “Thank you for purchase” pages)
Then the bot makes a judgement on which topics a page is about. Search engines are getting very good at reading and analysing content. The bot adds the page to an index about the topics and themes of the page, and a single page can be indexed for many different keywords and phrases. Pages in the index are ranked by relevance to the topics and keywords.
When an internet user searches a phrase, the search engine looks up the index and brings back the most relevant results within a fraction of a second.
The reason it’s so fast is because all the time consuming work of finding the pages and listing them together has already been done in advance. All the search engine has to do is open that section of the index to find appropriate answers and present them in search results. (You might see your search engine ranking position referred to as SERP.)
One thing to note is that search engines and bots can’t “see” images or videos, or “hear” audio files. So if your website includes images (and it should!) you should use Image Alt text and descriptive file names to indicate to bots what the images are about. Videos should be described in a paragraph or more of text, and you should include a brief written summary of audio files.
For more information about search engine crawling, see:
Deep Crawl: what is search engine crawling?
Search Engine Journal: Anatomy of a search engine crawler
Issues that affect crawling and your search engine rankings
There are some issues that make it hard for bots to crawl a website:
- Broken links force the bot to go back, noting that a page is not where it should be
- Pages buried deep beneath too many clicks make it hard for bots (and human users) to find information
- Low amount of text on a page so the search engine can’t work out what the page content is about
- Slow site speed affects how many pages a bot can crawl during a visit
- No site map – makes it harder for the search engine to crawl every page
- Orphaned pages – pages that are not connected to your main site navigation may not get crawled
- Changes – search engines won’t crawl static pages often. But news sites that are updated every minute, would be crawled constantly, to ensure up to date information. That’s why you can search “Fire in South Melbourne” and, if there’s a fire happening today, a news article from 10 minutes ago is more likely to be in the top spot than a story from a year ago.
To improve your rankings, fix issues like these on your website and make it easy for search engines to index your content.
Search engine ranking factors
Rumour has it that there are over 200 ranking factors that Google - and Yahoo! and Bing - use to decide which pages are the best match for your question. These companies keep their ranking factors a tightly held secret, but luckily, web experts have worked out the most important ranking factors to focus on.
Website security or HTTPS
Search engines have started penalising websites that are not secure, because poor security puts website visitors at risk. Read more about the importance of website security and SSL certificates here.
Page load speed
Just like us, search engines don’t tolerate slow page load speeds. Fast-loading pages get a boost in the rankings so it’s best to optimise your site’s speed. You can do this by compressing images and choosing options like “load text first” and fill in images later as the reader scrolls down.
Mobile friendly websites
Search engines know that most people use their mobiles for search now, so responsive website designs that are easy to use on a mobile or tablet get a boost in the rankings. Read more about mobile responsive website design here.
Optimised content
Back in the old days (like 2010!) a page could rank highly for a search term by simply stuffing hundreds of the same word or phrase into a page. Not any more. In fact, keyword stuffing is a negative ranking factor that will get your website in lots of trouble.
These days, search engines are incredibly sophisticated. They can read articles and opinion pieces to understand the tone and message of a page, not just individual keywords.
You can read more about search engine ranking factors here:
OptinMonster SEO ranking factors
How to determine your true organic Google ranking (this article gets a bit technical)
Let’s look at optimising content next.
What is SEO?
SEO, or search engine optimisation, is the process of making your website show up in search for specific keywords or phrases. You can adjust your website’s content to appeal to search engines for your target terms.
SEO is a long game and it needs continued tweaking. It takes patience and effort to reach the coveted top spots. But it’s worth it. The top organic listing gets over 30 percent of clicks!
Why you should care about search engine rankings
The goal is to appear among the top three results for your keyword. And this is no easy feat. With millions of results for competitive search terms, the top spots are a tiny percentage of all pages trying to rank for that phrase.
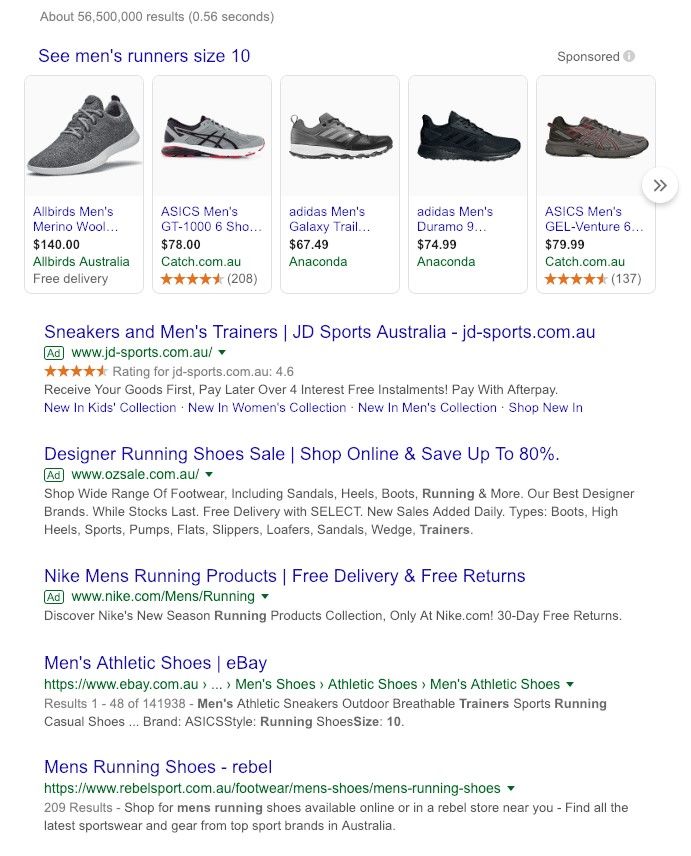
Here’s an example of searching for “Men’s runners size 10”. Let’s break down what it’s showing.
- There were over 56 million results for the search term “Men’s runners size 10”
- The top spots with images are paid listings – you can see they are marked Sponsored on the right. These companies have paid (potentially big bucks) to have their shoes shown for this exact phrase.
- The next three listings are also paid – you can see they have the word Ad on the left.
- Then there are the organic (unpaid) listings (this view shows the top two). The search engine has decided that these pages are the best match for the search keyword or phrase.
This example is from Google AU and results might be different on other search engines.
Also, results can be different for each individual user or device. That’s because Google takes into account a person’s location, if location data is turned on. Even if they didn’t specifically say “Men’s runners size 10 in Melbourne”, the search engine still knows that’s where they are. So you can see all the results above are for Australian websites rather than from US websites because this search came from Australia.
The search engines also take into account a user’s search history. So let’s say this user’s favourite brand is Nike, and they often visit the Nike shoes site, the search engine is more likely to show Nike shoes high in the results even if they didn’t specify Nike this time. It’s trying to be helpful and show the user what they want to see.
This is why it’s hard to check your own website ranking. You visit your own website a lot, and search engines know that. To check your ranking, it’s best to open a new “Incognito Window” or "Private Browsing" which almost completely ignores your personal search history to give you a more objective view of your website’s ranking.
These search engines are SMART. They’re constantly learning and evolving. Trying to be helpful and find your answers faster and convince customers to buy from the top listings.
As a website owner, that’s great news for you. The closer you can get to the top organic spots, the higher your click rate will be.
Here’s a chart from digital marketing research company Smart Insights, showing the average click rate of different positions. The top organic (unpaid) spot gets 30% of all clicks, 2nd spot gets 15%, with a sharp decline to 10th spot getting just 1% of clicks.
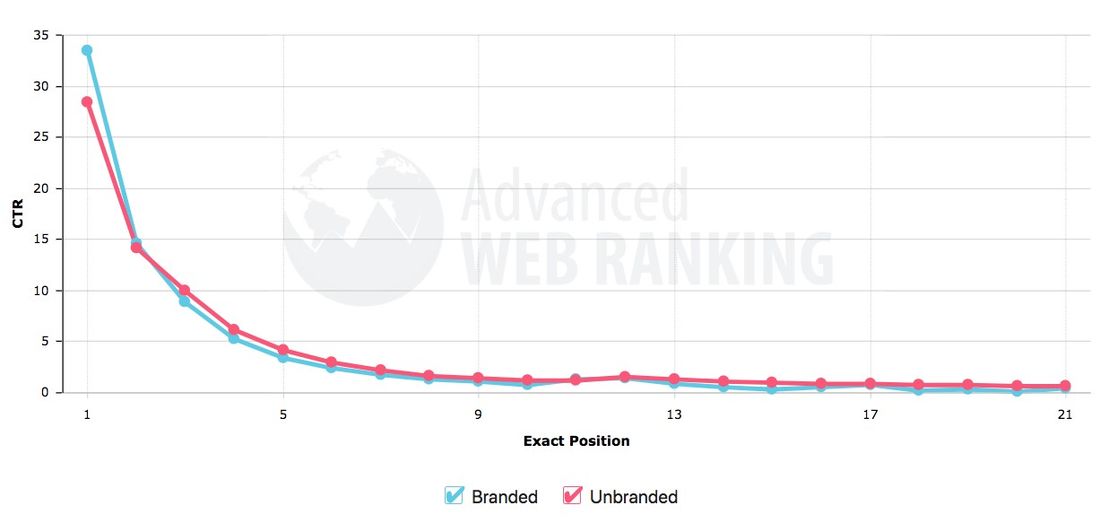
In reality, ranking in the top three spots for competitive and high traffic keywords is challenging. And it takes time to build up your rankings.
It’s much easier to rank for long tail keywords and phrases. Instead of aiming to rank for “jumper”, a kids’ clothing business could aim for “hand knitted wool kids jumper”. There’ll be fewer searches for that term, but also less competition. And the searchers who get specific with their searches know exactly what they want, and they’re getting very close to buying.
Luckily, there are a lot of things you can do to improve your rankings and be seen by more of your target customers.
Optimise your pages with keywords in the right places
A few tweaks and careful placement of the right words can do wonders for your search engine rankings.
Here we are searching for “Men’s runners size 10” again, and this is the top organic (unpaid) result:

You can see that the keywords (or related words) are in:
- Title Tag (blue line, about 60-70 characters)
- URL (green line)
- Meta description (grey lines, about 155 characters)
- H1 to H4 headings – the subheadings in the page (in this case it’s an eBay product listing)
- Main text – the bulk of the page’s content
You can see the search engine has highlighted the search words in the meta description to confirm that this result is a good match.
Also, although the search was for “runners”, the search engine knows the user might want to see results matching “athletic shoes”, “running shoes” or “casual shoes”. Clever! Search engines use synonyms and related words to provide helpful results.
It’s also clever enough to know the difference in user intent between “men’s runners” (shoes) and “male runners” (athletes) providing completely different results:
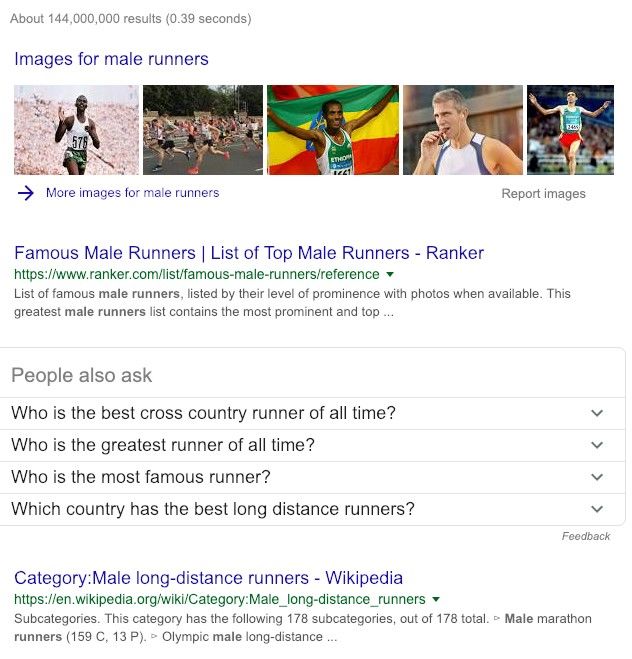
When you’re optimising your own website content, it’s important to know what your users are thinking about when they search. Consider using phrases about the problems that your product solves, as well as what it is.
For example, a beauty company can talk about “get smoother skin” or “look 10 years younger in 1 month” because that’s what the customer wants to achieve. That approach could capture different customers than the people who are searching directly for “loofah scrub” or “Vitamin E face moisturiser”, which is what the customer ends up buying.
Search engines are clever and they’ll help your customers find you, as long as you do the key things right.
Give SEO a try
Using the SEO tips above, try optimising some of your pages for specific keywords and phrases, and see how your rankings change over the next few months (remember to check using Incognito Mode for more accurate results).
And if you want to boost your rankings and need expert help, get in touch with our SEO experts on 1300 367 009.


